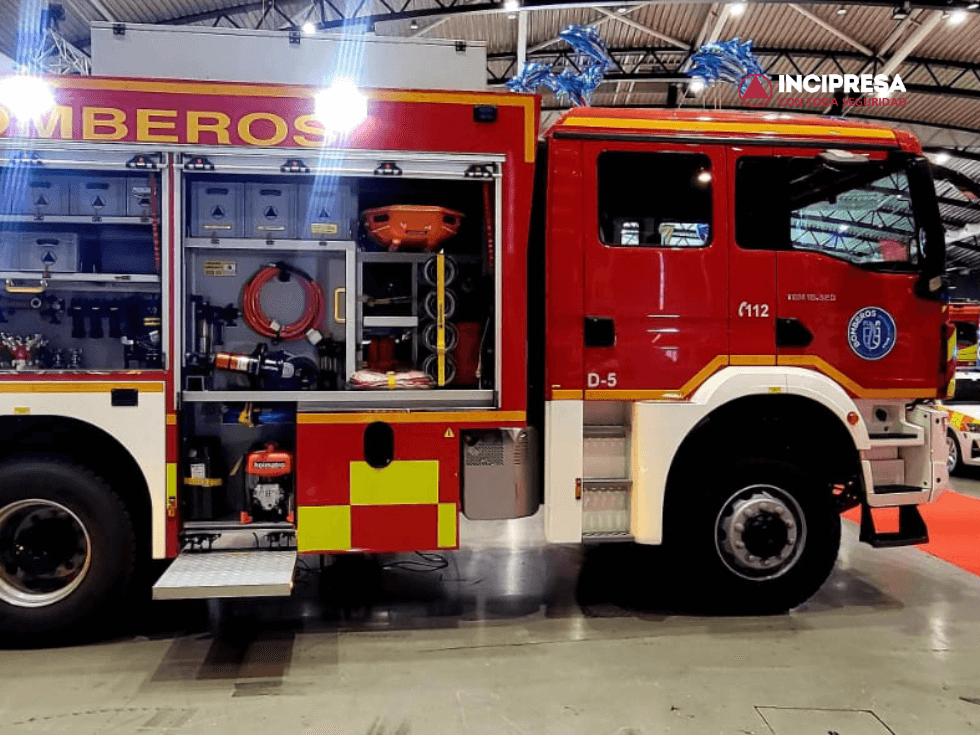
The Salamanca City Council has presented its new water tender…

Classification and types of firefighters in Spain
In everyday life, we constantly face risks and unpredictable situations that can threaten not only the safety of our properties but, more importantly, our lives. At the heart of mitigating these risks lies a profession as noble as it is challenging: the firefighter.
Their responsibilities go beyond putting out fires, expanding to a wide range of emergencies, from traffic accidents to natural disasters. Spain, with its geographic and climatic diversity, presents unique challenges that require a deep look at the different types of firefighters operating within its territory.
What does it take to be a firefighter in Spain?
Being a firefighter is embodying courage, resilience, and solidarity in service to the community. It requires a combination of physical ability, technical skill, and a firm ethical commitment. In addition to passing demanding physical tests, aspiring firefighters must show adaptability in adverse situations, clear communication skills, the ability to work in a team, and an empathetic disposition toward those they serve.
In Spain, the path to this profession begins with meeting a series of training requirements and going through a rigorous selection process.
Classification and types of firefighters in Spain
The classification of firefighters in Spain can be seen mainly from the perspective of their employment relationship with public administrations, dividing them into civil servant and non-civil servant firefighters.
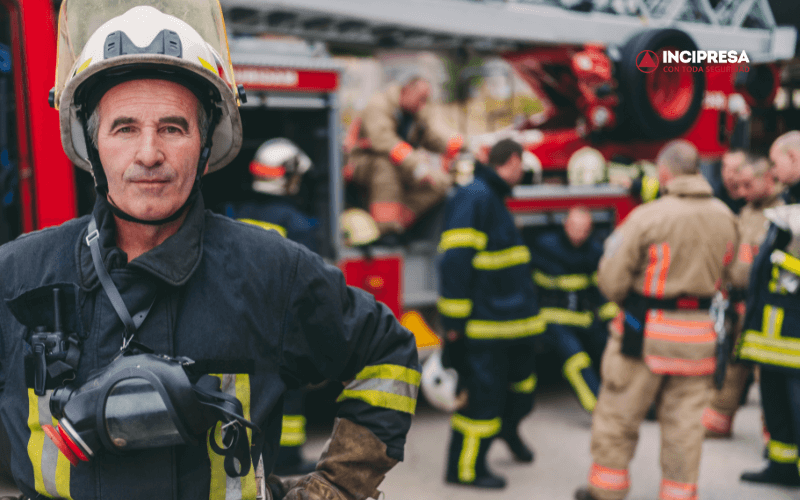

Civil Firefighters
Civil Firefighters access their position through a selection process that varies according to the entity that offers the position (city councils, autonomous communities, etc.). These include:
Municipal Firefighters:
Present in municipalities with more than 20,000 inhabitants, they are examples of first response to emergencies in urban areas.
Diputación and Consortium Firefighters:
They offer services in regions where municipalities cannot support their own fire department.
Autonomous Community Firefighters:
They act in areas not covered by municipal bodies, also attending to specific regional needs.
Forest Firefighters:
Specialized in the prevention and extinction of fires in natural environments, they are crucial given the forest wealth of Spain.
Military and Airport firefighters:
Those in charge of security at military installations and civil airports, respectively.
Non-civil service firefighters
These include volunteer firefighters, committed citizens who complement the work of official bodies, and private firefighters, professionals hired by companies to ensure fire safety at specific facilities.

The Importance of Training and Specialization
The robust firefighting system in Spain relies on continuous training and specialization to deal with an increasingly complex range of emergency situations.
Incipresa, recognized for its contribution in the field of rescue vehicles and equipment, plays a fundamental role in this ecosystem, providing not only tools, but also essential training for the development of advanced skills in rescue and extinction.
The different faces of intervention
From urban rescues to fighting forest fires, firefighters in Spain adapt to different environments and challenges.
The distribution and specialization of fire departments in the country ensure an efficient and specific response for each type of emergency. emergency.
The firefighting and rescue equipment that Incipresa offers are examples of this adaptation, complying with applicable regulations and representing the best in class worldwide.
Firefighters in Spain constitute a complex and multifaceted network of dedicated professionals committed to the safety and well-being of society. The country’s varied topography and climate demand an equally diverse and specialized response, finding in Incipresa a valuable ally. The essence of being a firefighter, with all that it implies in terms of sacrifice, courage and altruism, continues to inspire generations who aspire to join its ranks, thus ensuring that this vital service remains strong and resilient in the face of tomorrow’s challenges.